JACI:草花粉第5組主要變應(yīng)原Phl p 5的變應(yīng)原性研究
發(fā)布日期:2019-06-26
原標(biāo)題:IgE和T細胞對草花粉第5組主要變應(yīng)原Phl p 5的識別情況剖析
延伸閱讀
JACI
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2013.08.038
Background
The major timothy grass pollen allergen Phl p 5 belongs to the most potent allergens involved in hay fever and asthma.
Objective
This study characterized immune-dominant IgE- and T-cell–recognition sites of Phl p 5.
Methods
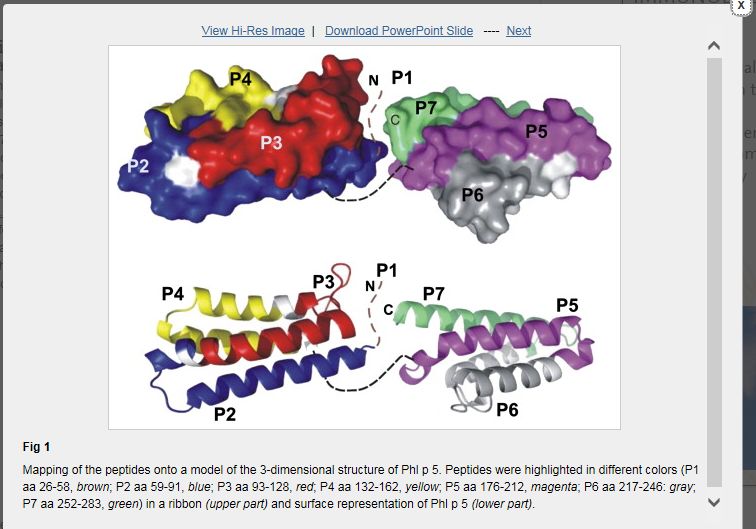
Seven peptides, P1 to P7 with a length of 31 to 38 amino acids that spanned the Phl p 5 sequence, were synthesized, characterized by circular dichroism spectroscopy, and tested for IgE reactivity, basophil activation, and T-cell reactivity. Carrier-bound peptides were studied for their ability to induce IgG antibodies in rabbits which recognize Phl p 5 or cross-reactive allergens from different grass species. Peptide-specific antibodies were tested for the capability to inhibit IgE reactivity to Phl p 5 and allergen-induced basophil activation of patients with allergy.
Results
The peptides exhibited no secondary structure and showed no IgE reactivity or relevant allergenic activity, indicating that Phl p 5 IgE epitopes are conformational. Except for P3, peptide-specific IgG antibodies blocked IgE binding to Phl p 5 of patients with allergy and cross-reacted with temperate grasses. IgE inhibition experiments and molecular modeling identified several clustered conformational IgE epitopes on the N- as well as C-terminal domain of Phl p 5. P4, which stimulated the strongest T-cell and cytokine responses in patients, was not part of the major IgE-reactive regions.
Conclusion
Our study shows an interesting dissociation of the major IgE- and T-cell–reactive domains in Phl p 5 which provides a basis for the development of novel forms of immunotherapy that selectively target IgE or T-cell responses.
All Authors:
Margarete Focke-Tejkl Raffaela Campana Renate Reininger Christian Lupinek Katharina Blatt Peter Valent Tea Pavkov-Keller Walter KellerWalter KellerRudolf Valenta


——浙大迪迅 譯
①梯牧草花粉主要過敏原Phl p 5是花粉熱和哮喘最強的過敏原之一。②本研究對Phl p 5的免疫優(yōu)勢IgE-和T細胞識別位點進行了研究。③合成了7個肽段,P1 - P7全長31 - 38個氨基酸,跨越Phl p 5序列,采用圓二色譜法對其進行了表征,并對IgE反應(yīng)活性、嗜堿性細胞活化和T細胞反應(yīng)活性進行了測試。研究了載體結(jié)合肽誘導(dǎo)兔IgG抗體的能力,該抗體能識別不同草種的Phl p 5或交叉反應(yīng)性變應(yīng)原。檢測肽特異性抗體抑制IgE對Phl p 5的反應(yīng)活性的能力,以及在過敏患者由過敏原引起的嗜堿性細胞活化的能力。④肽段無二級結(jié)構(gòu),無IgE反應(yīng)活性或相關(guān)致敏活性,表明Phl p 5 IgE表位具有構(gòu)象性。除P3外,肽段特異性IgG抗體阻斷了變態(tài)反應(yīng)性和與溫帶禾草發(fā)生交叉反應(yīng)的phlp5與IgE的結(jié)合。IgE抑制實驗和分子建模在phlp5的N-和c -末端區(qū)域發(fā)現(xiàn)了幾個聚集構(gòu)象的IgE表位。P4在患者中刺激T細胞和細胞因子的反應(yīng)最強,但不屬于主要的IgE反應(yīng)區(qū)域。⑤我們的研究顯示了一個有趣的現(xiàn)象:Phl p 5中的IgE-和T細胞反應(yīng)域是分離的,這為開發(fā)新的免疫療法提供了基礎(chǔ),這種療法可以選擇性地針對IgE或T細胞的反應(yīng)。
延伸閱讀
JACI
[IF:13.1]
Dissection of the IgE and T-cell recognition of the major group 5 grass pollen allergen Phl p 5DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2013.08.038
Background
The major timothy grass pollen allergen Phl p 5 belongs to the most potent allergens involved in hay fever and asthma.
Objective
This study characterized immune-dominant IgE- and T-cell–recognition sites of Phl p 5.
Methods
Seven peptides, P1 to P7 with a length of 31 to 38 amino acids that spanned the Phl p 5 sequence, were synthesized, characterized by circular dichroism spectroscopy, and tested for IgE reactivity, basophil activation, and T-cell reactivity. Carrier-bound peptides were studied for their ability to induce IgG antibodies in rabbits which recognize Phl p 5 or cross-reactive allergens from different grass species. Peptide-specific antibodies were tested for the capability to inhibit IgE reactivity to Phl p 5 and allergen-induced basophil activation of patients with allergy.
Results
The peptides exhibited no secondary structure and showed no IgE reactivity or relevant allergenic activity, indicating that Phl p 5 IgE epitopes are conformational. Except for P3, peptide-specific IgG antibodies blocked IgE binding to Phl p 5 of patients with allergy and cross-reacted with temperate grasses. IgE inhibition experiments and molecular modeling identified several clustered conformational IgE epitopes on the N- as well as C-terminal domain of Phl p 5. P4, which stimulated the strongest T-cell and cytokine responses in patients, was not part of the major IgE-reactive regions.
Conclusion
Our study shows an interesting dissociation of the major IgE- and T-cell–reactive domains in Phl p 5 which provides a basis for the development of novel forms of immunotherapy that selectively target IgE or T-cell responses.
All Authors:
Margarete Focke-Tejkl Raffaela Campana Renate Reininger Christian Lupinek Katharina Blatt Peter Valent Tea Pavkov-Keller Walter KellerWalter KellerRudolf Valenta
2019-5-17 Article
創(chuàng)建過敏性疾病的科研、科普知識交流平臺,為過敏患者提供專業(yè)診斷、治療、預(yù)防的共享平臺。

 杭州浙大迪迅生物基因工程有限公司
杭州浙大迪迅生物基因工程有限公司

