Clin Exp Allergy: 通過(guò)兒童哮喘轉(zhuǎn)錄組群的遺傳圖譜來(lái)確定特型嚴(yán)重亞型
發(fā)布日期:2018-11-13
原標(biāo)題:兒童哮喘轉(zhuǎn)錄組群的遺傳圖譜確定特型嚴(yán)重亞型
延伸閱讀

Clinical & Experimental Allergy
DOI: 10.1111/cea.13175
Abstract:
Background: Previous studies have defined transcriptomic subtypes of adult asthma using samples of induced sputum and bronchial epithelium; however, those procedures are not readily applicable in the clinic,especially for childhood asthma.
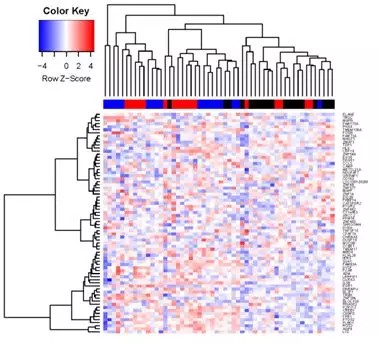
Methods: Gene expression of PBMC from 133 asthmatic children and 11 healthy controls was measured with Illumina microarrays. We applied the k-means clustering algorithm of 2048 genes to assign asthmatic children into clusters. Genes with differential expression between asthma clusters and healthy controls were used to investigate whether they could identify severe asthma of children and adults.
Results: We identified three asthma clusters with distinct inflammatory profiles in peripheral blood. Cluster 1 had the highest eosinophil count. Cluster 2 showed lower counts of both eosinophils and neutrophils.Cluster 3 had the highest neutrophil count, and the poorest treatment control. Compared with other patients, Cluster 3 exhibited a unique gene expression pattern which was associated with changes in the glucocorticoid signaling and activation of the T helper 1/T helper 17 (TH1/TH17) immune pathways. In the validation studies, an 84-gene signature could identify severe asthma in children on leukocytes, as well as severe asthma in adults on CD8+ T cells.
Conclusions: Gene expression profiling of PBMC is useful for the identification of TH1/TH17-mediated asthma with poor treatment control. PBMC and CD8+ T cells could be important targets for the investigation and identification of severe asthma.
First Author:
Y.-L. Yeh
Correspondence:
Institute of Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine, College of Public Health, National Taiwan University
All Authors:
Y.-L. Yeh, M.-W. Su, B.-L. Chiang, Y.-H. Yang, C.-H. Tsai, Y. L. Lee


——來(lái)自浙大迪迅
?、?先前有研究定義了成人哮喘的轉(zhuǎn)錄子亞型,然而這并不容易應(yīng)用于臨床,尤其是兒童哮喘;② 應(yīng)用Illumina芯片技術(shù)檢測(cè)133例哮喘患兒和11例健康對(duì)照的PBMC基因表達(dá)情況;③采用了2048個(gè)基因的k-means聚類算法將哮喘患兒分組;④ 84基因特征可以識(shí)別兒童重癥哮喘的白細(xì)胞,以及成人重癥哮喘的CD8+T細(xì)胞;⑤ PBMC和CD8+T細(xì)胞可作為重癥哮喘研究和鑒別的重要靶點(diǎn)
延伸閱讀

Clinical & Experimental Allergy
[IF:5.158]
Genetic Profiles of Transcriptomic Clusters of Childhood Asthma Determine Specific Severe SubtypeDOI: 10.1111/cea.13175
Abstract:
Background: Previous studies have defined transcriptomic subtypes of adult asthma using samples of induced sputum and bronchial epithelium; however, those procedures are not readily applicable in the clinic,especially for childhood asthma.
Methods: Gene expression of PBMC from 133 asthmatic children and 11 healthy controls was measured with Illumina microarrays. We applied the k-means clustering algorithm of 2048 genes to assign asthmatic children into clusters. Genes with differential expression between asthma clusters and healthy controls were used to investigate whether they could identify severe asthma of children and adults.
Results: We identified three asthma clusters with distinct inflammatory profiles in peripheral blood. Cluster 1 had the highest eosinophil count. Cluster 2 showed lower counts of both eosinophils and neutrophils.Cluster 3 had the highest neutrophil count, and the poorest treatment control. Compared with other patients, Cluster 3 exhibited a unique gene expression pattern which was associated with changes in the glucocorticoid signaling and activation of the T helper 1/T helper 17 (TH1/TH17) immune pathways. In the validation studies, an 84-gene signature could identify severe asthma in children on leukocytes, as well as severe asthma in adults on CD8+ T cells.
Conclusions: Gene expression profiling of PBMC is useful for the identification of TH1/TH17-mediated asthma with poor treatment control. PBMC and CD8+ T cells could be important targets for the investigation and identification of severe asthma.
First Author:
Y.-L. Yeh
Correspondence:
Institute of Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine, College of Public Health, National Taiwan University
All Authors:
Y.-L. Yeh, M.-W. Su, B.-L. Chiang, Y.-H. Yang, C.-H. Tsai, Y. L. Lee
2018-10-25 Article
創(chuàng)建過(guò)敏性疾病的科研、科普知識(shí)交流平臺(tái),為過(guò)敏患者提供專業(yè)診斷、治療、預(yù)防的共享平臺(tái)。

 杭州浙大迪迅生物基因工程有限公司
杭州浙大迪迅生物基因工程有限公司

