Allergy:雙胞胎兒童哮喘的遺傳研究
發(fā)布日期:2018-11-26
原標題:雙胞胎兒童哮喘遺傳力和遺傳證明的關(guān)聯(lián)研究
延伸閱讀

Allergy
DOI: 10.1111/all.12783
Abstract:
Background: Although the genetics of asthma has been extensively studied using both quantitative and molecular genetic analysis methods, both approaches lack studies specific to the childhood phenotype and including other allergic diseases.This study aimed to give specific estimates for the heritability of childhood asthma and other allergic diseases, to attempt to replicate findings from genomewide association studies (GWAS) for childhood asthma and to test the same variants against other allergic diseases.
Methods: In a cohort of 25 306 Swedish twins aged 9 or 12 years, data on asthma were available from parental interviews and population-based registers. The interviews also inquired about wheeze, hay fever, eczema, and food allergy. Through structural equation modeling, the heritability of all phenotypes was calculated. A subset of 10 075 twins was genotyped for 16 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) selected from previous GWAS; these were first tested for association with asthma and significant findings also against the other allergic diseases.
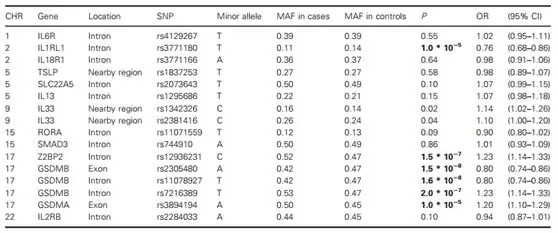
Results: The heritability of any childhood asthma was 0.82 (95% CI 0.79–0.85).For the other allergic diseases, the range was approximately 0.60–0.80. Associations for six SNPs with asthma were replicated, including rs2305480 in the GSDMB gene (OR 0.80, 95% CI 0.74–0.86, P = 1.5*108; other significant associations all below P = 3.5*10^4). Of these, only rs3771180 in IL1RL1 was associated with any other allergic disease (for hay fever, OR 0.64, 95% CI 0.53–0.77, P = 2.5*10^6).
Conclusions: Asthma and allergic diseases of childhood are highly heritable, and these high-risk genetic variants associated specifically with childhood asthma,except for one SNP shared with hay fever.
First Author:
V. Ullemar
Correspondence:
Vilhelmina Ullemar, Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics
All Authors:
V. Ullemar, P. K. E. Magnusson, C. Lundholm, A. Zettergren, E. Melen , P. Lichtenstein&C. Almqvist


——來自浙大迪迅
?、?哮喘的遺傳學(xué)已經(jīng)廣泛地使用定量和分子遺傳學(xué)分析方法進行研究,但是兩種方法都缺乏針對兒童表型和其他過敏性疾病特異性的研究;② 納入25306對9歲或12歲的瑞典雙胞胎;③ 對10075對雙胞胎的子集進行16個單核苷酸多態(tài)性(SNP)的基因分型,這些單核苷酸多態(tài)性選自先前的GWAS;④ 兒童哮喘的遺傳力為0.82;⑤ IL1RL1中只有rs3771180與其他過敏性疾病相關(guān)(對于花粉熱)。
延伸閱讀

Allergy
[IF:6.048]
Heritability and confirmation of genetic association studies for childhood asthma in twinsDOI: 10.1111/all.12783
Abstract:
Background: Although the genetics of asthma has been extensively studied using both quantitative and molecular genetic analysis methods, both approaches lack studies specific to the childhood phenotype and including other allergic diseases.This study aimed to give specific estimates for the heritability of childhood asthma and other allergic diseases, to attempt to replicate findings from genomewide association studies (GWAS) for childhood asthma and to test the same variants against other allergic diseases.
Methods: In a cohort of 25 306 Swedish twins aged 9 or 12 years, data on asthma were available from parental interviews and population-based registers. The interviews also inquired about wheeze, hay fever, eczema, and food allergy. Through structural equation modeling, the heritability of all phenotypes was calculated. A subset of 10 075 twins was genotyped for 16 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) selected from previous GWAS; these were first tested for association with asthma and significant findings also against the other allergic diseases.
Results: The heritability of any childhood asthma was 0.82 (95% CI 0.79–0.85).For the other allergic diseases, the range was approximately 0.60–0.80. Associations for six SNPs with asthma were replicated, including rs2305480 in the GSDMB gene (OR 0.80, 95% CI 0.74–0.86, P = 1.5*108; other significant associations all below P = 3.5*10^4). Of these, only rs3771180 in IL1RL1 was associated with any other allergic disease (for hay fever, OR 0.64, 95% CI 0.53–0.77, P = 2.5*10^6).
Conclusions: Asthma and allergic diseases of childhood are highly heritable, and these high-risk genetic variants associated specifically with childhood asthma,except for one SNP shared with hay fever.
First Author:
V. Ullemar
Correspondence:
Vilhelmina Ullemar, Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics
All Authors:
V. Ullemar, P. K. E. Magnusson, C. Lundholm, A. Zettergren, E. Melen , P. Lichtenstein&C. Almqvist
2018-11-18 Article
創(chuàng)建過敏性疾病的科研、科普知識交流平臺,為過敏患者提供專業(yè)診斷、治療、預(yù)防的共享平臺。

 杭州浙大迪迅生物基因工程有限公司
杭州浙大迪迅生物基因工程有限公司

