JACI:過敏性肺炎:吸入多種抗原引起的纖維性肺泡炎
發(fā)布日期:2019-04-30
原標(biāo)題:過敏性肺炎:吸入多種抗原引起的纖維性肺泡炎
延伸閱讀
JACI
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2018.09.040
Abstract:
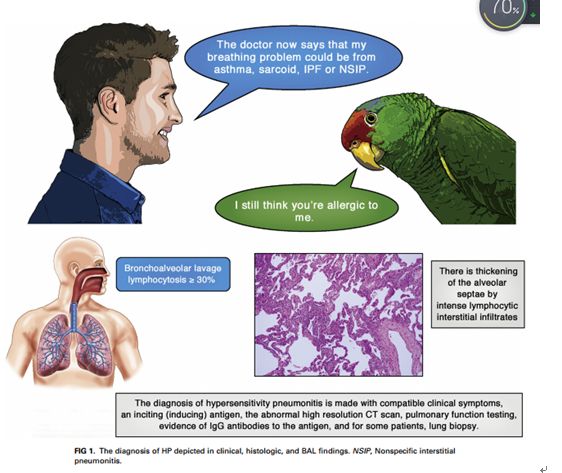
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is a TH1 lymphocyte–biased fibrosing alveolitis caused by antigens ranging from avian excreta, fungi, thermophilic bacteria, and protozoa to reactive chemicals found in the workplace. Mimicking a viral syndrome, acute exposures to inciting antigens cause abrupt onset of nonproductive cough, dyspnea, and chills with arthralgias or malaise usually from 4 to 8 hours later so that the temporal relationship between antigen exposure and symptoms might be unsuspected. The histology of HP reveals prominent lymphocyte infiltrates that thicken the alveolar septa with poorly formed granulomas or giant cells. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid demonstrates greater than 20% lymphocytes in nearly all patients. Abnormalities on high-resolution computed tomographic examinations range from nodular centrilobular opacities in acute/subacute disease to increased reticular markings and honeycombing fibrosis, which typically are predominant in the upper lobes, in patients with advanced disease. Descriptors include “mosaic” attenuation and ground-glass opacities. Repeated episodes can result in nodular pulmonary infiltrates and suspected nonspecific interstitial pneumonia or idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clinicians require a high level of suspicion to make an early diagnosis of HP before extensive pulmonary fibrosis or restrictive lung disease has occurred.an expert panel of the American Thoracic Society commented that, ‘‘For patients with suspected interstitial lung disease in whom BAL is performed, we suggest that lymphocyte subset analysis NOT be a routine component of BAL cellular analysis.’’ What constitutes a ‘‘high level of confidence’’ in diagnosis is a matter of debate. In the absence of a diagnostic test, the diagnosis is made with compatible clinical symptoms, an inciting (inducing) antigen, an abnormal high-resolution computed tomographic (CT) scan, pulmonary function testing, evidence of IgG antibodies to the antigen, and, for some patients, lung biopsy.
Authors:
Paul A. GreenbergerMD


——浙大迪迅 譯
過敏性肺炎(HP)是一種TH1淋巴細胞偏向性纖維性肺泡炎,由多種抗原引起,包括禽排泄物、真菌、嗜熱細菌和原生動物,以及工作場所發(fā)現(xiàn)的反應(yīng)性化學(xué)物質(zhì)。與病毒綜合征相似,急性暴露于刺激抗原可導(dǎo)致突然出現(xiàn)無生產(chǎn)能力的咳嗽、呼吸困難、伴有關(guān)節(jié)痛的寒戰(zhàn)或不 適,通常在4至8小時后發(fā)生,因此抗原暴露與癥狀之間的時間關(guān)系可能沒有受到懷疑。HP組織學(xué)表現(xiàn)為明顯的淋巴細胞浸潤,使肺泡間隔增厚,伴有肉芽腫或巨細胞。幾乎所有患者的支氣管肺泡灌洗液中淋巴細胞都超過20%。高分辨率計算機斷層檢查的異常情況:從急性/亞急性疾病的結(jié)節(jié)性小葉中心混濁到晚期疾病患者典型的以上葉為主的網(wǎng)狀斑紋和蜂窩狀纖維化。描述詞匯包括“鑲嵌樣”衰減和毛玻璃混濁。反復(fù)發(fā)作可導(dǎo)致結(jié)節(jié)性肺浸潤和可疑的非特異性間質(zhì)性肺炎或特發(fā)性肺纖維化。在廣泛的肺纖維化或限制性肺疾病發(fā)生之前,臨床醫(yī)生需要高度懷疑才能對HP做出早期診斷。美國胸科學(xué)會的一個專家小組評論道:“對于懷疑患有間質(zhì)性肺病的患者進行BAL,我們建議淋巴細胞亞群分析不是BAL細胞分析的常規(guī)組成部分。什么構(gòu)成了對診斷的“高度自信”是一個有爭議的問題。在沒有診斷試驗的情況下,診斷需符合臨床癥狀、刺激(誘導(dǎo))抗原、異常高分辨率計算機斷層掃描(CT)、肺功能檢測、抗原特異性IgG抗體的證據(jù)、部分患者需肺活檢。
延伸閱讀
JACI
[IF:13.1]
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: A fibrosing alveolitis produced by inhalation of diverse antigenshttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2018.09.040
Abstract:
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is a TH1 lymphocyte–biased fibrosing alveolitis caused by antigens ranging from avian excreta, fungi, thermophilic bacteria, and protozoa to reactive chemicals found in the workplace. Mimicking a viral syndrome, acute exposures to inciting antigens cause abrupt onset of nonproductive cough, dyspnea, and chills with arthralgias or malaise usually from 4 to 8 hours later so that the temporal relationship between antigen exposure and symptoms might be unsuspected. The histology of HP reveals prominent lymphocyte infiltrates that thicken the alveolar septa with poorly formed granulomas or giant cells. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid demonstrates greater than 20% lymphocytes in nearly all patients. Abnormalities on high-resolution computed tomographic examinations range from nodular centrilobular opacities in acute/subacute disease to increased reticular markings and honeycombing fibrosis, which typically are predominant in the upper lobes, in patients with advanced disease. Descriptors include “mosaic” attenuation and ground-glass opacities. Repeated episodes can result in nodular pulmonary infiltrates and suspected nonspecific interstitial pneumonia or idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clinicians require a high level of suspicion to make an early diagnosis of HP before extensive pulmonary fibrosis or restrictive lung disease has occurred.an expert panel of the American Thoracic Society commented that, ‘‘For patients with suspected interstitial lung disease in whom BAL is performed, we suggest that lymphocyte subset analysis NOT be a routine component of BAL cellular analysis.’’ What constitutes a ‘‘high level of confidence’’ in diagnosis is a matter of debate. In the absence of a diagnostic test, the diagnosis is made with compatible clinical symptoms, an inciting (inducing) antigen, an abnormal high-resolution computed tomographic (CT) scan, pulmonary function testing, evidence of IgG antibodies to the antigen, and, for some patients, lung biopsy.
Authors:
Paul A. GreenbergerMD
2019-4-16 Review
創(chuàng)建過敏性疾病的科研、科普知識交流平臺,為過敏患者提供專業(yè)診斷、治療、預(yù)防的共享平臺。

 杭州浙大迪迅生物基因工程有限公司
杭州浙大迪迅生物基因工程有限公司

