JACI:哮喘和非哮喘兒童IgE對螨蟲組份不同的識別能力
發(fā)布日期:2018-12-24
原標題:哮喘和非哮喘兒童IgE對螨蟲組份不同的識別能力
延伸閱讀
JACI:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2015.03.024
Abstract:
Background
House dust mites (HDMs) represent one of the most important inducers of respiratory allergies worldwide.
Objective
We sought to investigate the IgE and IgG reactivity profiles to a comprehensive panel of HDM allergens in children with allergic asthma and to compare them with those of nonasthmatic atopic children.
Methods
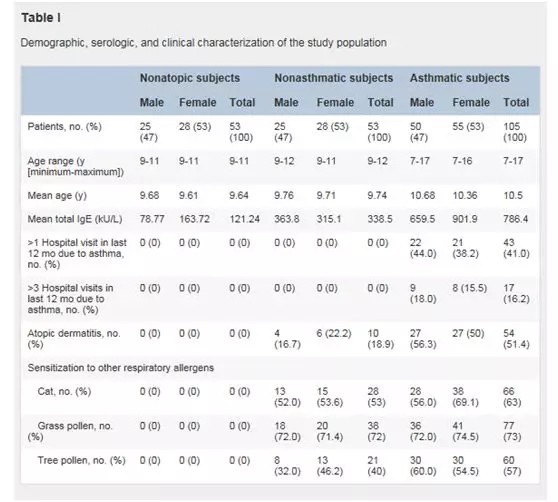
Sera from clinically well-characterized asthmatic children with HDM allergy (n = 105), nonasthmatic children (n = 53), and nonatopic nonasthmatic children (n = 53) were analyzed for IgE and IgG reactivity to a panel of 7 HDM allergens (nDer p 1, rDer p 2, rDer p 5, rDer p 7, rDer p 10, rDer p 21, and rDer p 23) by means of allergen microarray technology.
Results
Asthmatic children with HDM allergy more frequently showed an IgE response to each of the HDM allergens and recognized more allergens than nonasthmatic children with HDM allergy. Furthermore, IgE levels to certain HDM allergens (nDer p 1, P = .002; rDer p 2, P = .007; rDer p 5, P = .031; and rDer p 23, P < .001) were significantly higher in asthmatic children than in children without asthma. By contrast, fewer asthmatic children showed IgG reactivity to HDM allergens than nonasthmatic children, but allergen-specific IgG levels were comparable.
Conclusion
The IgE and IgG reactivity profiles to HDM allergens, as well as IgE levels to certain allergen components, differed considerably between children with and without asthmatic symptoms caused by HDM allergy. In fact, asthmatic children were characterized by an expanded IgE repertoire regarding the numbers of recognized allergen components and by increased specific IgE levels.
All Author:
Yvonne Resch, MSc, Sven Michel, MSc, Michael Kabesch, MD, Christian Lupinek, MD, Rudolf Valenta, MD, Susanne Vrtala, PhD


——來自浙大迪迅
?、傥輭m螨(HDMs)是世界范圍內(nèi)最重要的呼吸道過敏誘因之一。②我們試圖研究過敏性哮喘兒童中HDM過敏原的IgE和IgG反應(yīng)譜,并將其與非哮喘性特應(yīng)性兒童進行比較。③用一系列戶塵螨過敏原(nDer p 1, rDer p 2, rDer p 5, rDer p 7, rDer p 10, rDer p 21, and rDer p 23)通過過敏原微陣列技術(shù)對來自明確診斷的戶塵螨過敏哮喘兒童 (n = 105),非哮喘兒童(n = 53),非過敏且非哮喘兒童 (n = 53)的血清 進行了IgE結(jié)合分析。④戶塵螨過敏的哮喘患兒對每種戶塵螨過敏原的IgE反應(yīng)頻率更高,識別出的過敏原多于對戶塵螨過敏的非哮喘患兒。此外,某些戶塵螨過敏原的IgE水平(nDer p 1, P = .002; rDer p 2, P = .007; rDer p 5, P = .031; and rDer p 23, P < .001 rDer p23、p < 0.001)哮喘患兒顯著高于非哮喘患兒。相比之下,哮喘患兒對戶塵螨過敏原有IgG反應(yīng)活性的人數(shù)低于非哮喘患兒,但過敏原特異性IgG水平相當。⑤對戶塵螨過敏原的IgE和IgG反應(yīng)譜,以及對某些過敏原組分的IgE水平,在由戶塵螨過敏引起哮喘和非哮喘兒童之間有很大差異。事實上,哮喘患兒的特點是IgE結(jié)合過敏原組份的數(shù)量增加,且特異性IgE水平升高。
延伸閱讀
JACI:
[IF:13.1]
Different IgE recognition of mite allergen components in asthmatic and nonasthmatic childrenhttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2015.03.024
Abstract:
Background
House dust mites (HDMs) represent one of the most important inducers of respiratory allergies worldwide.
Objective
We sought to investigate the IgE and IgG reactivity profiles to a comprehensive panel of HDM allergens in children with allergic asthma and to compare them with those of nonasthmatic atopic children.
Methods
Sera from clinically well-characterized asthmatic children with HDM allergy (n = 105), nonasthmatic children (n = 53), and nonatopic nonasthmatic children (n = 53) were analyzed for IgE and IgG reactivity to a panel of 7 HDM allergens (nDer p 1, rDer p 2, rDer p 5, rDer p 7, rDer p 10, rDer p 21, and rDer p 23) by means of allergen microarray technology.
Results
Asthmatic children with HDM allergy more frequently showed an IgE response to each of the HDM allergens and recognized more allergens than nonasthmatic children with HDM allergy. Furthermore, IgE levels to certain HDM allergens (nDer p 1, P = .002; rDer p 2, P = .007; rDer p 5, P = .031; and rDer p 23, P < .001) were significantly higher in asthmatic children than in children without asthma. By contrast, fewer asthmatic children showed IgG reactivity to HDM allergens than nonasthmatic children, but allergen-specific IgG levels were comparable.
Conclusion
The IgE and IgG reactivity profiles to HDM allergens, as well as IgE levels to certain allergen components, differed considerably between children with and without asthmatic symptoms caused by HDM allergy. In fact, asthmatic children were characterized by an expanded IgE repertoire regarding the numbers of recognized allergen components and by increased specific IgE levels.
All Author:
Yvonne Resch, MSc, Sven Michel, MSc, Michael Kabesch, MD, Christian Lupinek, MD, Rudolf Valenta, MD, Susanne Vrtala, PhD
2018-12-21 Article
創(chuàng)建過敏性疾病的科研、科普知識交流平臺,為過敏患者提供專業(yè)診斷、治療、預(yù)防的共享平臺。

 杭州浙大迪迅生物基因工程有限公司
杭州浙大迪迅生物基因工程有限公司

